A Comprehensive Study on Heavy Metal Contamination in Irrigation Water and Soil from Farmland Located Near Dravyavati River in Jaipur

DOI:
https://doi.org/10.54060/a2zjournals.jmce.64Keywords:
Atomic Absorption Spectrometry, below limit of quantification, Dravyavati riverAbstract
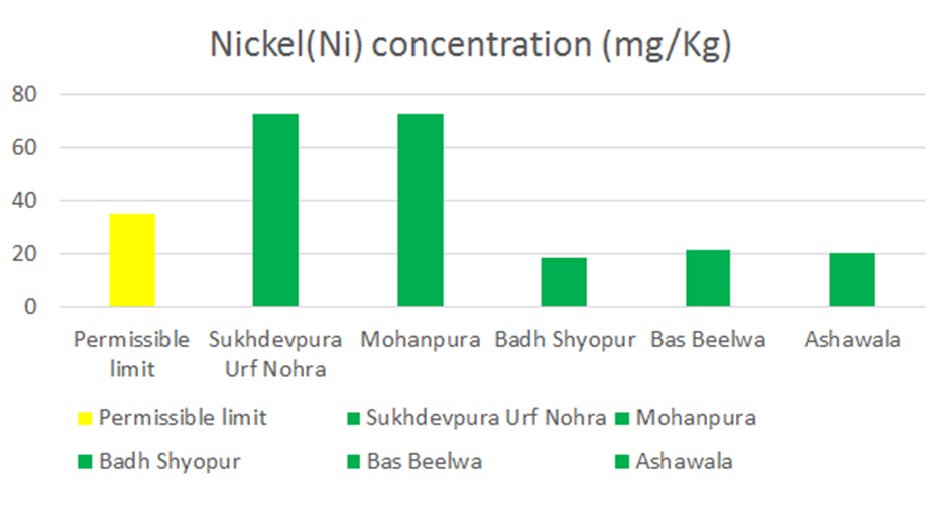
The environmental issue today is the contamination of river water and soil by heavy metals. Various pollutants are generated and continuously increasing because of various human activities, which are affecting the environment. Numerous varieties of chemical substances are being discharged into the water and soil through different resources and processes, which affect the environmental quality in multiple ways. Highly toxic metals present in water and soil pose a high number of health risks to humans and animals. Heavy metals are among the primary pollutants. In this study, five soil samples were analyzed for heavy metals, including nickel, mercury, arsenic, copper, lead, and zinc. Additionally, five water samples were collected and examined such as copper (Cu), lead (Pb), nickel (Ni), mercury (Hg), zinc (Zn), and arsenic (As) for the detection of heavy metals in them. Soil samples collected from five different vil-lages, and water samples were obtained from four villages near the Dravyavati River, including Mohanpura, Baas Beelwa, Baadh Shyopur, Ashawala, and Sukhdevpura Urf Nohra. The samples were analyzed using Atomic Absorption Spectrometry (AAS), a technique used to detect trace element concentrations in soil and water. The study's findings indicated that copper and lead levels in all five soil samples were below the permissible limits set by the WHO (1996), while zinc levels exceeded the permissible limits in all samples. Nickel concentrations were higher in the soil of Sukhdevpura Urf Nohra and Mohanpura but lower in the other three villages. Mercury and arsenic were below BLQ level when all five samples were analysed. However, industrial ef-fluents discharged into the environment around the Dravyavati River Basin, now known as Amanishah Nallah, have severely impacted the basin's ecosystem. Industri-alization has had a detrimental effect on the soil irrigated by its waters.
Downloads
References
A. Al-Hussaini, A. H. Al-Atrushi, and M. I. Abdul Kareem, "The environmental assessment of heavy metal pollution of Di-yala River in city of Baghdad, Iraq," Journal of Applied Water Science, vol. 8, pp. 1-6, May 2022.
D. Mudgal, "Assessment of heavy metals toxicity in contaminated soil and vegetables irrigated with industrial and sewage effluent in Jaipur city and its surrounding area," Ph.D. dissertation, Univ. of Rajasthan, Jaipur, India, May 2022.
M. Patel, "Investigation and physico-chemical characterization of groundwater quality of Jodhpur district, Western Raja-sthan," Ph.D. dissertation, Univ. of Rajasthan, Jodhpur, India, 2018.
R. Jagariya, "To study the impact of effluent of sewage and industries in East Southern part of Amanishah Nala on soil with reference to agriculture and irrigational purposes," Ph.D. dissertation, Univ. of Rajasthan, Jaipur, India, 2018.
A. Mitryasova, V. Boyko, and S. Pasternak, "Integrated environmental assessment of the surface waters pollution," in 17th International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConference, vol. 7, no. 3, 2017. [Online]. Available: http://dx.doi.org/10.5593/sgem2017H/33/S12.029, Jan. 2021.
M. Islam, A. S. Islam, M. S. M. Rahman, and S. H. Arefin, "Environmental assessment of water and soil contamination in Rajakhali Canal of Karnaphuli River (Bangladesh) impacted by anthropogenic influences," Journal of Applied Water Sci-ence, vol. 7, pp. 997-1010, July 2015.
S. O. Fakayode, "The impact assessment of industrial effluents on water quality of the receiving Alaro River in Ibadan, Nigeria," African Journal of Environmental Assessment and Management, vol. 10, pp. 209-214, May 2017.
A. Mehta, "Physico-chemical and microbial studies of groundwater of Sanganer, Tehsil Jaipur Rajasthan and comparison with other regions," Ph.D. dissertation, Poornima Univ., Jaipur, India, 2016.
O. Phiri, G. B. Mumba, P. Z. Moyo, and W. Kadewa, "The impact of industrial effluents on water quality of receiving river in urban areas of Malawi," International Journal of Environment Science and Technology, vol. 2, pp. 237-244, May 2014.
P. Venugopal, K. Venkatesan, and A. T. Ramalingam, "The environmental impact assessment and seasonal variation of the groundwater in the vicinity of river Adyar, Chennai," Journal of Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, vol. 9, pp. 81-97, June 2013.
M. A. Hussain and R. J. Rao, "The effect of industrial effluents on surface water quality of Patancheru, Andhra Pradesh," Journal of Current World Environment, vol. 8, pp. 445-454, Nov. 2013.
M. S. Islam, M. K. Ahmed, and M. A. Molla, "The effects of solid waste and industrial effluents on water quality of Turag River at Konabari industrial area, Gazipur, Bangladesh," Journal of Environmental Science and Natural Resources, vol. 5, pp. 213-218, April 2013.
F. M. Azom, M. A. Mahmud, M. S. Sultana, S. M. Rahman, and A. Islam, "The environmental impact assessment (EIA) of tanneries in Hazaribagh, Bangladesh," International Journal of Environmental Science and Development, vol. 3, pp. 152-156, May 2012.
T. C. Ogwueleka, "Assessment of the quality of water and identification of pollution sources of Kaduna River in Niger state, Nigeria," Journal of Water and Environment, vol. 28, pp. 229, Nov. 2012.
P. Walakira and W. Okumu, "The impact of industrial effluents on water quality of streams in Nakawa-Ntinda, Uganda," Journal of Applied Science, vol. 15, pp. 154-159, August 2011.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
CITATION COUNT
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Babusha Mittal, Priti Kaushik

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
























