Performance Evaluation of Traction Motors Using Simulation Model Considering Different Driving Cycles

DOI:
https://doi.org/10.54060/a2zjournals.jmce.61Keywords:
Electric Vehicle, Traction Motor, Driving Cycle, Matlab Simulink, Induction Motor, Switched Reluctance Motor, Urban Drive Cycle, Highway Drive CycleAbstract
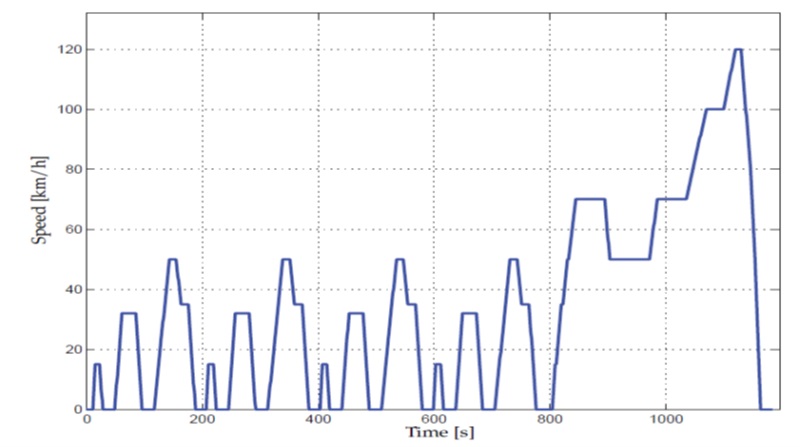
The abstract outlines the fundamental principles underlying traction motor operation, elucidating the role of these motors in converting electrical energy into mechanical motion for propelling EVs. Various types of traction motors, including DC motors, permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSMs), induction motors, and switched reluctance motors (SRMs), are discussed, highlighting their unique features and performance attributes. In this research project we will explore the key performance metrics used to assess traction motor efficiency and effectiveness. Parameters such as torque-speed characteristics, power density, efficiency, and thermal management are analysed in detail, emphasizing their significance in determining overall vehicle performance and range. Electric Vehicle model is simulated for each type of traction motor for same drive cycles and other vehicle parameters being constant for each simulation model and evaluating traction motor’s performance by comparing their results. In this thesis, we develop both a vehicle dynamics model and a vehicle load model, taking into account various road conditions and drive cycles.
Downloads
References
L. Kumar and S. Jain, “Electric propulsion system for electric vehicular technology: A review,” Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., vol. 29, pp. 924–940, 2014.
K. M. Rahman, B. Fahimi, G. Suresh, A. V. Rajarathnam, and M. Ehsani, “Advantages of switched reluctance motor applica-tions to EV and HEV: design and control issues,” IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl., vol. 36, no. 1, pp. 111–121, 2000.
B. Bilgin and A. Emadi, “Electric Motors in Electrified Transportation: A step toward achieving a sustainable and highly efficient transportation system,” IEEE Power Electron. Mag., vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 10–17, 2014.
Y. M. Ehsani and A. Gao, Modern Electric, Hybrid Electric, And Fuel Cell Vehicles: Fundamentals, Theory, and Design. Boca Raton: CRC press, 2009.
S. Bikram Dutta, Mathematical MATLAB Model and Performance Analysis of Asynchronous Machine. 2017.
A. Varsha and M. M. Shah, Study of Fuel Economy and Emissions for Converted Plug-In Parallel Hybrid Electric Vehicle Versus Conventional Diesel Vehicle on Standard Driving Cycles.
S. Soylu, Ed., Electric Vehicles - Modelling and Simulations. InTech, 2011.
Indian Drive Cycles and RDE Program for Effective Emission Norms, Controls and Policies, by Mukesh Sharma and Rajesh Singh Department of Civil Engineering.
M. Hoyer, "http://www.machinedesign.com," Applications Engineer HBM Inc., 18 Nov. 2013.
P. Fajri, V. A. K. Prabhala, and M. Ferdowsi, “Emulating on-road operating conditions for electric-drive propulsion sys-tems,” IEEE Trans. Energy Convers., vol. 31, no. 1, pp. 1–11, 2016.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
CITATION COUNT
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Umesh Singh, Atul Gaikwad, Neha Gupta

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
























