Purification of Water Using Nanotechnology

DOI:
https://doi.org/10.54060/jmce.v3i1.27Keywords:
Nanotechnology, reverse osmosis, photocatalytic titania, sustainabilityAbstract
One of the most crucial ingredients for life on earth is water. It has played a crucial role in the development of human civilizations, starting with the emergence of the first aspect of existence in seawater. The demand for clean water is universal and essential to all human species. But at the moment, pure water supplies are being poisoned. Water quality and society's level of development have recently been linked. The safety of drinking water has been put in jeopardy by several chemical and biological pollutants. Alternatives for decontaminating and reusing water are among the most desired solu-tions to address the issues of water shortage and the escalating disputes over this essen-tial resource. A significant issue is the buildup of organic debris and its residues in wastewater. Significant progress has been achieved in using the chemistry of nano-materials for purifying water as a result of the realization of the molecular nature of pollution in drinking water. Due to its capacity to produce precise, structurally controlled materials for such needs, nanotechnology offers exceptional potential in filtering appli-cations. By extending the idea of clean, inexpensive, and sustainable water to the eco-system as a whole, we point out that cities may live and breathe comfortably by using such technology. Sustainability in clean water may be achieved by comprehending the major environmental issues facing the world and investigating potential solutions from new nanotechnologies.
Downloads
References
M.P. Ajith & M.K. James, “Impact of Chamravattam regulator cum bridge on Bharathapuzhariver and adjacent areas,” Indian Journal of Economics and Development, vol.1, no.4, pp.1-6, January 2016.
M.P. Ajith, M. Aswathi, E. Priyadarshini et al., “Recent Innovations of Nanotechnology in Water Treatment: A Comprehensive Review,” Bioresource Technology, vol.342, no.4, 2021.
M.A. Shah, and T. Ahmed, “Principles of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology”. Narosa Publishing House: New Delhi, pp.34-47, 2011.
N. Savage & M.S. Diallo, “Nanomaterials and water purification: Opportunities and challenges,” Journal of Nanoparticle Re-search, vol.7, pp.331–342, October 2005.
K. Gupta, S. Bhattacharya, D.J. Chattopadhyay, et al., “Ceria associated manganese oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, characteriza-tion and arsenic(V) sorption behavior,” Chemical Engineering Journal, vol.172, no.1, pp.219-229 ,2011.
W.X. Zhang, “Nano-scale iron particles for environmental remediation: an overview,” Journal of Nanoparticle research, vol.5, pp.323–332, 2003.
M.P. Ajith, E. Priyadarshini, P. Rajamani, “Effective and selective removal of heavy metals from industrial effluents using sus-tainable Si–CD conjugate based column chromatography,” Bioresource Technology, vol.314, Oct 2020.
A. Varghese, “A comparative risk approach to assessing point-of-use water treatment systems in developing countries Comparative risk assessment and environmental decision making, “NATO science series IV Earth and Environment Sci-ence NAIV, vol.38, pp.99–112, 2005.
P.H. Gleick, “Global freshwater resources: soft-path solutions for the 21st century Science,”vol. 302, no.5650, pp.1524–1528, 2003.
C.N. Haas, “Disinfection in the twenty-first century,” American. Water Works Association Journal, vol.92, no.2, pp.72-73, Feb 2000.
E.D. Mintz, F.M. Reiff and R.V Tauxe, “Safe water treatment and storage in the home: a practical new strategy to prevent wa-terborne disease,” Jama, vol.273, no.12, pp.948–953, March 1995.
S.W. Krasner, H. S. Weinberg, S.D. Richardson, et al., “Occurrence of a new generation of disinfection byproducts,” Environ-mental Science and technology, vol.40, no.23, pp.7175–7185, 2006.
Q. Li, S. Mahendra, D. Y. Lyon, et al., “Antimicrobial nanomaterials for water disinfection and microbial control: potential appli-cations and implications,” Water Research, vol.42, no.18, pp. 4591–4602, 2008.
A. Danion, J. Disdier, C. Guillard, et al., “Characterization and study of a single-TiO2-coated optical fiber reactor,” Applied Ca-talysis B: Environmental, vol.52, no.3, pp.213–223, April 2004.
R.J. Narayan, S.P. Adiga, M. J. Pellin et al., “Atomic layer deposition-based functionalization of materials for medical and envi-ronmental health applications,” Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci., vol.368, pp.2033–2064, 2010.
R. J. Narayan, N. A. M. Riviere, R. L. Brigmon, et al., “Atomic layer deposition of TiO 2 thin films on nanoporous alumina tem-plates: medical applications,” JOM, vol.6, pp.12–16, 2009.
V. B. Vouk, “Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals,” Elsevier-North-Holland Biomedical Press, pp.1-47, 1979.
B. Nowack, “Pollution prevention and treatment using nanotechnology, “Nanotechnology, pp.1–15, 2008.
S. O. Obare and G. J. Meyer, “Nanostructured materials for environmental remediation of organic contaminants in water,” J. Environmental Science Health Part A, vol.39, pp.2549–2582, 2004.
N. Savage and M. S. Diallo, “Nanomaterials and water purification: opportunities and challenges,” Journal of Nanoparticle Re-search, vol.7, pp.331–342, 2005.
J. Theron, J. A. Walker and T. E. Cloete, “Nanotechnology and water treatment: applications and emerging opportunities,” Crit-ical Reviews in Microbiology, vol.34, pp.43–69, 2008.
M. N. Khan & I. Tlili, “AInnovative Thermodynamic parametric investigation of gas and steam bottoming cycles with heat ex-changer and heat recovery steam generator: energy and exergy analysis,”. Energy Reports, vol.4, pp.497–506, 2018.
B. G. Agaie, I. Khan, Z. Yacoob, et al., “A novel technique of reduce order modelling without static correction for transient flow of non-isothermal hydrogen-natural gas mixture,” Result inPhysics, vol.10, pp.532–540 ,2018.
A. Khalid, I. Khan, A. Khan, et al., “Case study of MHD blood flow in a porous medium with CNTS and thermal analysis,” Case Studies in Thermal Engineering, vol 12, pp.374–380,2018.
A.R. Alharbi, I. M. Alarifi, W. S. Khan, et al., “Highly hydrophilic electrospunpolyacrylonitrile/polyvinypyrrolidonenanofibers incorporated with gentamicin as filter medium for dam water and wastewater treatment,” Journal of Membrane and Separa-tion Technology, vol.5, no.2, pp.38–56, 2016.
J. Kim & B. V. der. Bruggen, “The use of nanoparticles in polymeric and ceramic membrane structures: review of manufactur-ing procedures and performance improvement for water treatment,” Environmental Pollution, vol.158, no.7, pp.2335–2349, 2010.
J. Bae, I. Baek & H. Choi, “Mechanically enhanced PES electro spun nano fiber membranes (ENMs)for microfiltration: the ef-fects of ENM properties on membrane performance,” Water Research, vol.105, pp.406–412, 2016.
R. Asmatulu, “Enhancement of detectability characteristic of fine silica particles,” Turkish Journal of Engineering and Environ-mental Science, vol.26, no.6, pp.513–520, 2002.
P. I. Dolez, N. Bodila, J. Lara, et al., “Personal protective equipment against nanoparticles,” International Journal of Nanotech-nology, vol.7, no.1, pp.99–117, 2009.
R. Asmatulu, “Improvement of detectability characteristics of hydrophobic fine particles by air bubble entrapments, “Powder Technology, vol.186, no.2, pp.184–188, 2007.
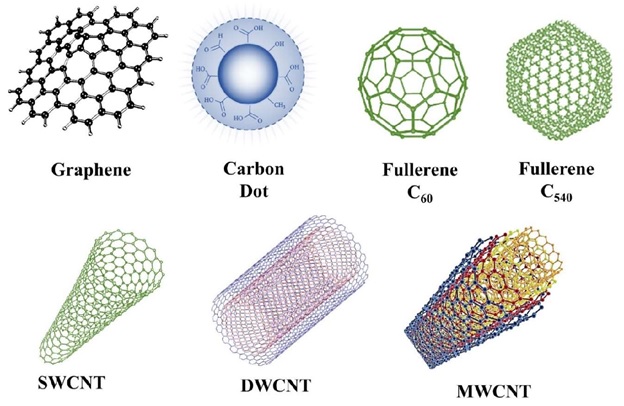
M. S. Mauter, M. Elimelech, “Environmental applications of carbon-based nanomaterials,” Environmental science & technolo-gy, vol.42, no.16, pp.5843-5859, 2008.
M. P. Ajith, E.Priyadarshini, P. Rajamani, “Effective and selective removal of heavy metals from industrial effluents using sus-tainable Si–CD conjugate based column chromatography,” Bioresource Technology, vol.134, Oct 2020.
B. I. Kharisov, H. R. Dias, O. V. Kharissova, “Nanotechnology-based remediation of petroleum impurities from water,” Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, vol.122, pp.705-718, 2014.
Y. Zhang, Z. R. Tang, X. Fu, et al., “TiO2− graphenenanocomposites for gas-phase photocatalytic degradation of volatile aromatic pollutant is TiO2− graphene truly different from other TiO2− carbon composite materials,” ACS nano, vol.4, no.12, pp.7303-7314, 2010.
L. Bashambu, R. Singh, J. Verma, “Metal/metal oxide nanocomposite membranes for water purification,” Materials Today: Pro-ceedings, vol.44, pp.538-545, 2021.
C. Santhosh, V. Velmurugan, G.J. Jeong et al., “Role of nanomaterials in water treatment applications: a review,” Chemical En-gineering Journal, vol.306, pp.1116-1137, 2016.
S. K. Das, A. K. Guha, G. Sekaran, et al., “Nano-silica fabricated with silver nanoparticles: antifouling adsorbent for efficient dye removal, effective water disinfection and biofouling control,” Nanoscale, vol.5, no.12, pp.5549-5560, 2013.
O.S. Tsekhmistrenko, V.S. Bityutskyy, S. I. Tsekhmistrenko et al., “Nanotechnologies and environment: A review of pros and cons, “Ukrainian Journal of Ecology, vol.10, no.3, pp.162– 172, 2020.
Y. Ying, W. Ying, Q. Li, et al., “Recent advances of nanomaterial-based membrane for water purification,” Applied Materials Today, vol.7, pp.144-158, 2017.
M. P. Ajith, M. Aswathi, E. Priyadarshini et al., “Recent Innovations of Nanotechnology in Water Treatment: A Comprehensive Review,” Bioresource Technology, vol.342, no.22, 2021.
US Bureau of Reclamation and Sandia National Laboratories, “Desalination and water purification technology roadmap a report of the executive committee Water Purification,” 2003.
V. D. B. Bruggen, C. Vandercasteele, “Removal of pollutants from surface water and groundwater by nanofiltration: Overview of the possible applications in the drinking water industry,” Environmental Pollution, vol.122, no.3, pp.435-445, April 2003.
A. F. Reguillon, G. Lebuzit, J. Fooz, et al., “Selective concentration of uranium from seawater by nanofiltration,” Industrial and engineering chemistry research, vol.42, no.23, pp.5900–5904, 2003.
M. S. Mohsen, J. O. Jaber, M. D. Afonso, “Desalination of brackish water by nanofiltration and reverse osmosis, “Desalination, vol.157, no.1-3, pp.167–167, August 2003.
S. Peltier, E. Cotte, D. Gatel, et al., “Nanofiltration improvements of water quality in a large distribution system,” Water Science and Technology: Water Supply, vol.3, no.1-2, pp.193–200, 2003.
A. Srivastava, O. N. Srivastava, S. Talapatra, et al., “Carbon nanotube filters Nature Materials Rajan, “C.S. Nanotechnology, vol.3, no.9, pp .610–614. 32.,2004.
M. A. Shah, T. Ahmed, “Principles of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology,” Narosa Publishing House New Delhi India, vol.21, no.4, pp.34-47, 2011.
C. S Rajan, “Nanotechnology in groundwater remediation,” International Journal of Environmental Science and Development, vol.2, no.3, pp.182-187, June 2011
W. X. Zhang, “Nano-scale iron particles for environmental remediation: an overview,” Journal of Nanoparticle research, vol.5, pp.323–332, August 2003.
USEPA, “Nanotechnology and Radiation clean up,” Retrieved from: 2013. https://www.epa.gov/remedytech/nanotechnology-site-remediation-fact-sheet
R. Singh, V. Misra, R. P. Singh, “Remediation of Cr (VI) contaminated soil by Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticles (nZVI) entrapped in Calcium Alginate Beads, “Proceedings of 2nd International Conference on Environmental Science and Development IPCBEE, vol.4, pp.162-165, 2011.
USEPA (US Environmental Protection Agency), “Technology Innovation Office Permeable Reactive Barriers,” Retrieved from:2003.
B. Nowack, T. D. Bucheli, “Occurrence, behavior and effects of nanoparticles in the environment,” Environmental Pollution, vol.150, no.1, pp.5-22, November 2007.
F. H. Frimmel and R. Niessner, “Nanoparticles in the water cycle: Properties analysis and environmental,” relevance Springer: USA, vol.400, pp2679-2680, 2011.
Minnesota Rural Water Association, “Advancing the science of water: AwwaRF and membrane process, “Retrieved from: 2013. http://www.waterrf.org/resources/State
J. Kidd, P. Westerhoff, A.D. Maynard, “Public perceptions for the use of nanomaterials for in-home drinking water purification devices,” Nano Impact, vol.18, 2020.
M. Zeng, M. Chen, D. Huang, et al., “Engineered two dimensional nanomaterials: an emerging paradigm for water purification and monitoring,” Mater Horiz, vol.8, pp.758-802, 2020.
T. A. Saleh, “An overview of nanomaterials for water technology,” Adv. Nanomaterial for Water Engineering Treatment and Hydraulics, pp.1–12 ,2017.
S. Ahuja, “Handbook of Water Purity and Quality,” Elsevier, Second Edition, vol.55, pp.339– 357, 2021.
M.B. Mohamed “Low-cost nanomaterials for water desalination and purification,” In Final Technical Report, United Nations UNSCO, pp.1-28, 2011.
Q. Li, S. Mahendra, D.Y. Lyon, et al., “Antimicrobial nanomaterials for water disinfection and microbial control: potential appli-cations and implications,” Water Research, vol.42, no.18, pp. 4591–4602, November 2008.
M. Nasrollahzadeh, M. Sajjadi, S. Iravani, et al., “Green-synthesized nano catalysts and nanomaterials for water treatment: Cur-rent challenges and future perspectives,” Journal of Hazardous Materials, vol.401, January 2021.
X.Y. Xue, R. Cheng, L. Shi, et al., “Nanomaterials for water pollution monitoring and remediation,” Environ. Chem. Lett., vol.15, no.1, pp.23–27, 2017.
C. Santhosh, V. Velmurugan, G. Jacob, et al., “Role of nanomaterials in water treatment applications: a review,” Chemical Engi-neering Journal, vol.306, pp.1116–1137, 2016.
D. Wang, “A critical review of cellulose-based nanomaterials for water purification in industrial processes, “Cellulose, vol.26, no.2, pp.687–701, 2018.
Y. Zhu, X. Liu, Y. Hue et al., “Behavior remediation effect, and toxicity of nanomaterials in water environments, “Environmental Research, vol.174, pp.54–60, 2019.
R. Wilson, G. George, A.J. Jose, “Polymer membranes reinforced with carbon-based nanomaterials for water purification,” New polymer nanocomposites for environmental remediation Elsevier, pp.457–468, 2018.
A.E. Burakov, I.V. Burakova, E.V. Galunin, et al., “Handbook of Ecomaterials, “ Springer International Publishing Cham, pp.1–20, 2017.
Z. Wang, A. Wu, L. C. Ciacchi, et al., “Recent advances in nano porous membranes for water purification,” Nanomaterials, vol.8, no.2, 2018.
F. Lu, D. Astruc, N. Catalysts et al., “Nanomaterials for water remediation from organic pollutants, “Coordination Chemistry Re-views, vol.408, 2020,
R.D. Ambashta, M. Sillanpä, “Water purification using magnetic assistance a review, “Journal of Hazardous Material, vol.180, no.1-3, pp.38-49, 2010.
R.S. Dongre, “Rationally Fabricated Nanomaterials for Desalination and Water Purification, Synthesis and Applications,” Novel Nanomaterials, pp.27 -11038–11049, 2018.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
CITATION COUNT
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Akshita Agarwal, Anushka Goyal, Pragya Paliwal, Arti Mishra, Swati Singh

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
























